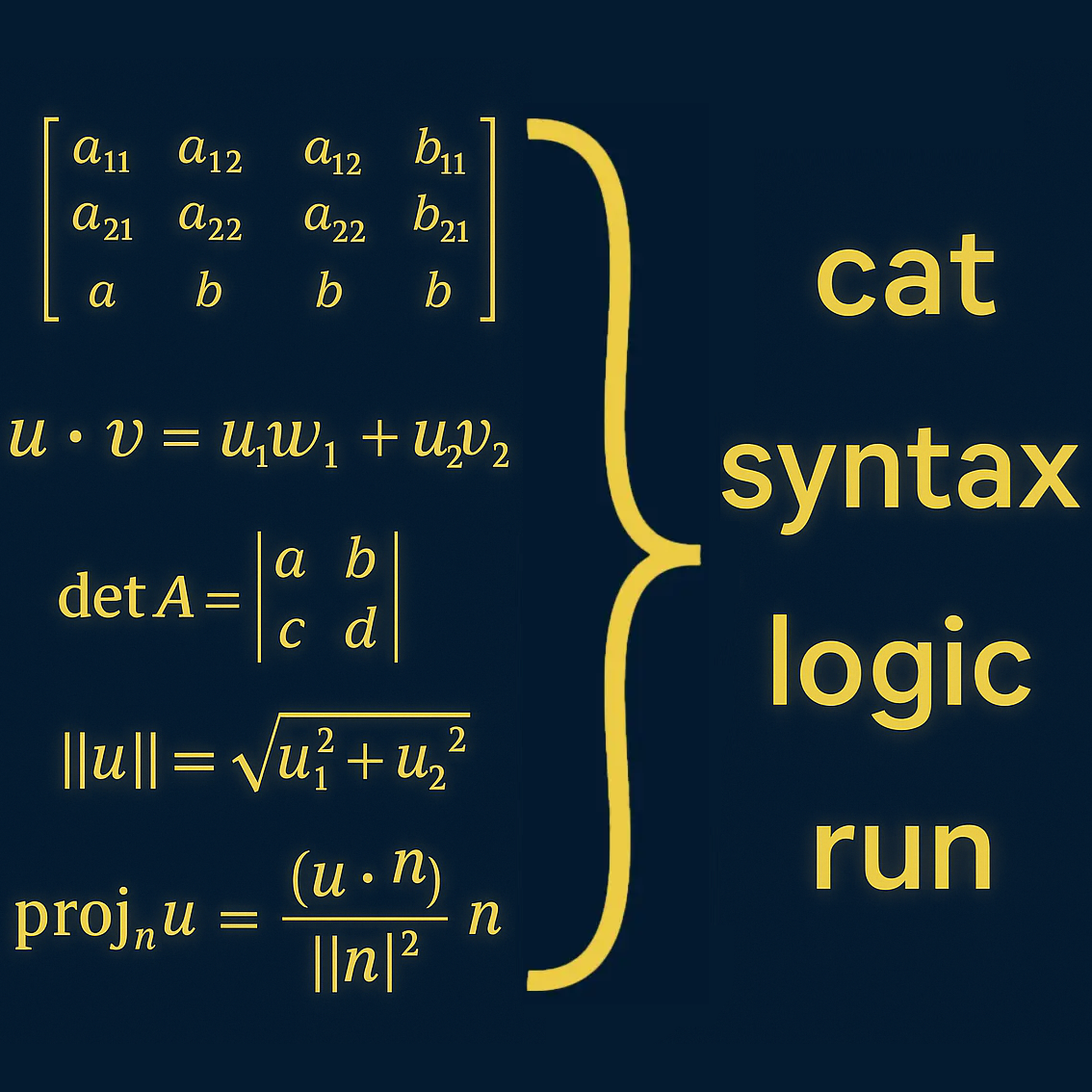
When you enter a sentence into a Large Language Model (LLM) such as ChatGPT or Claude , the model does not process words as language. It represents them as numbers.
Each word, phrase, and code token becomes a vector — a list of real-valued coordinates within a high-dimensional space. Relationships between meanings are captured not by grammar or logic but by geometry. The closer two vectors lie, the more similar their semantic roles appear to the model.
This is the mathematical foundation of large language models: linear algebra. Matrix multiplication, vector projection, cosine similarity, and normalization define how the model navigates this vast space of meaning. What feels like understanding is actually the alignment of high-dimensional vectors governed by probability and geometry.
“Linear algebra and geometry do more than support AI; they create its language of meaning.”
